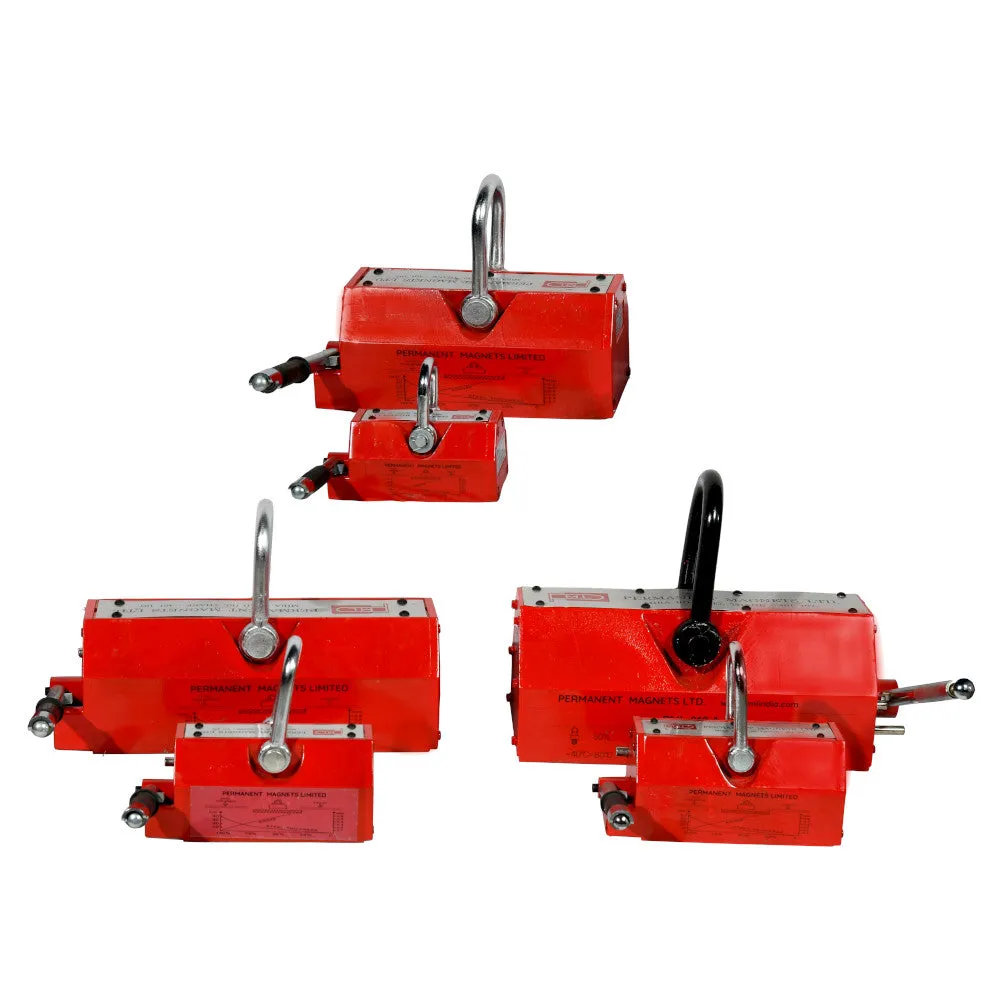
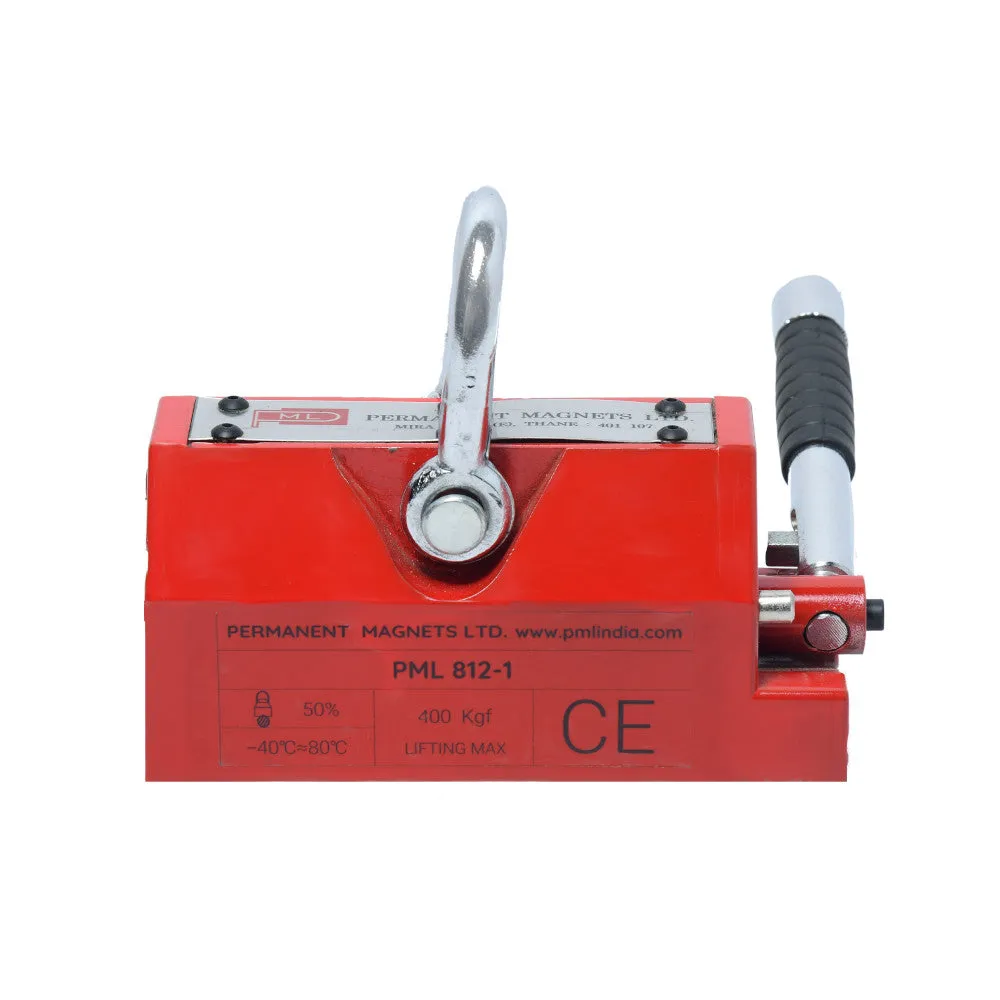
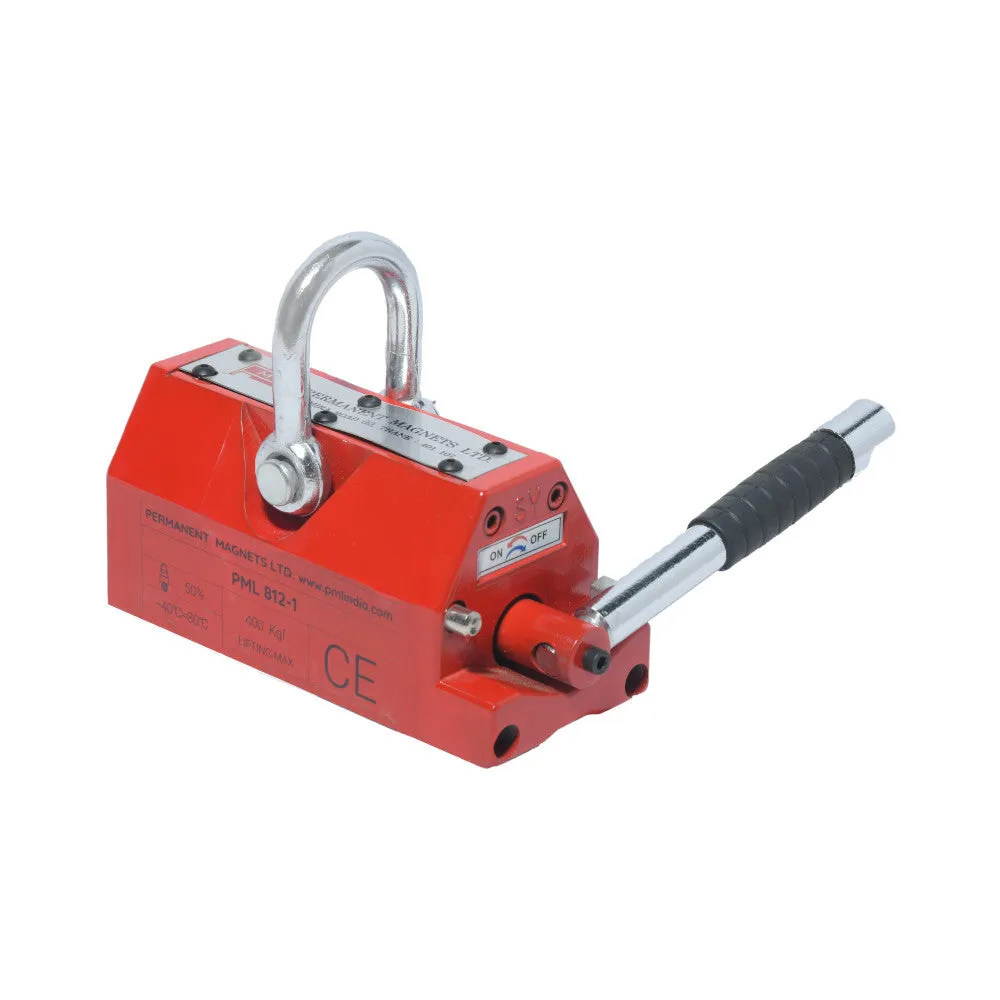
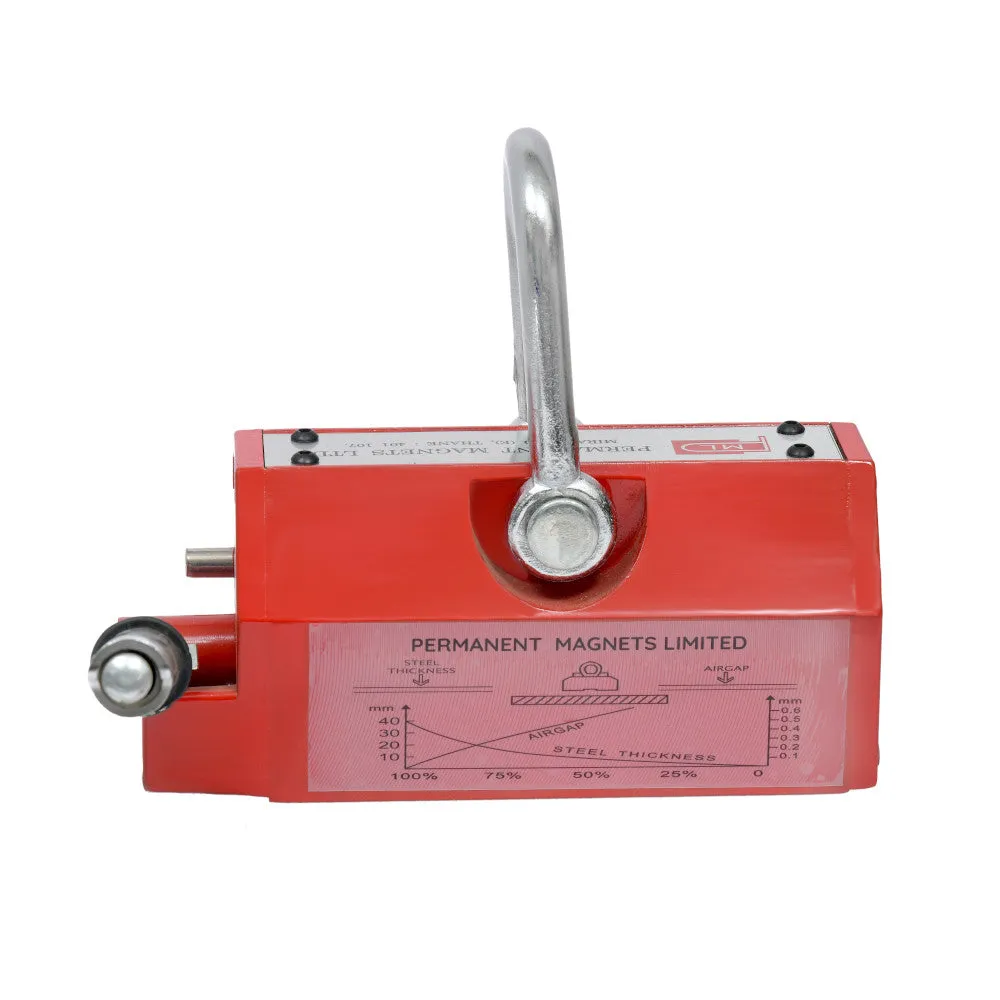
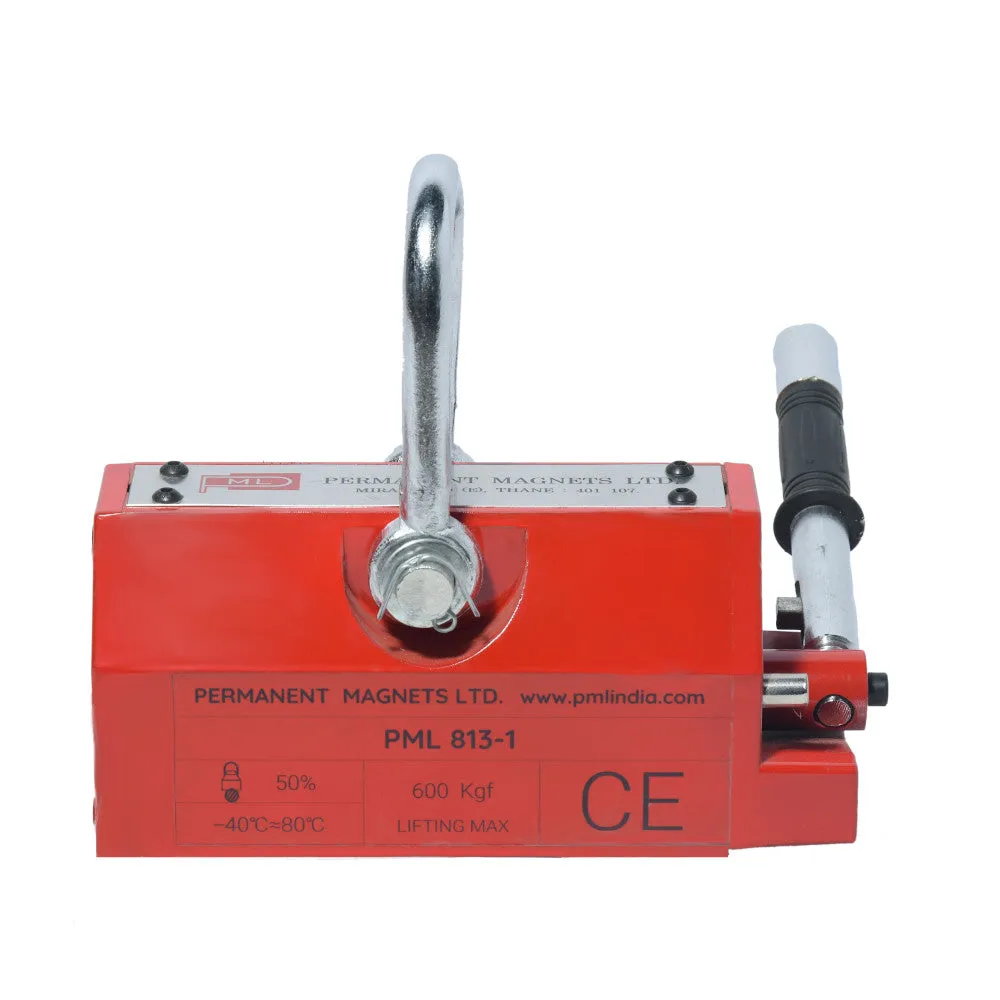
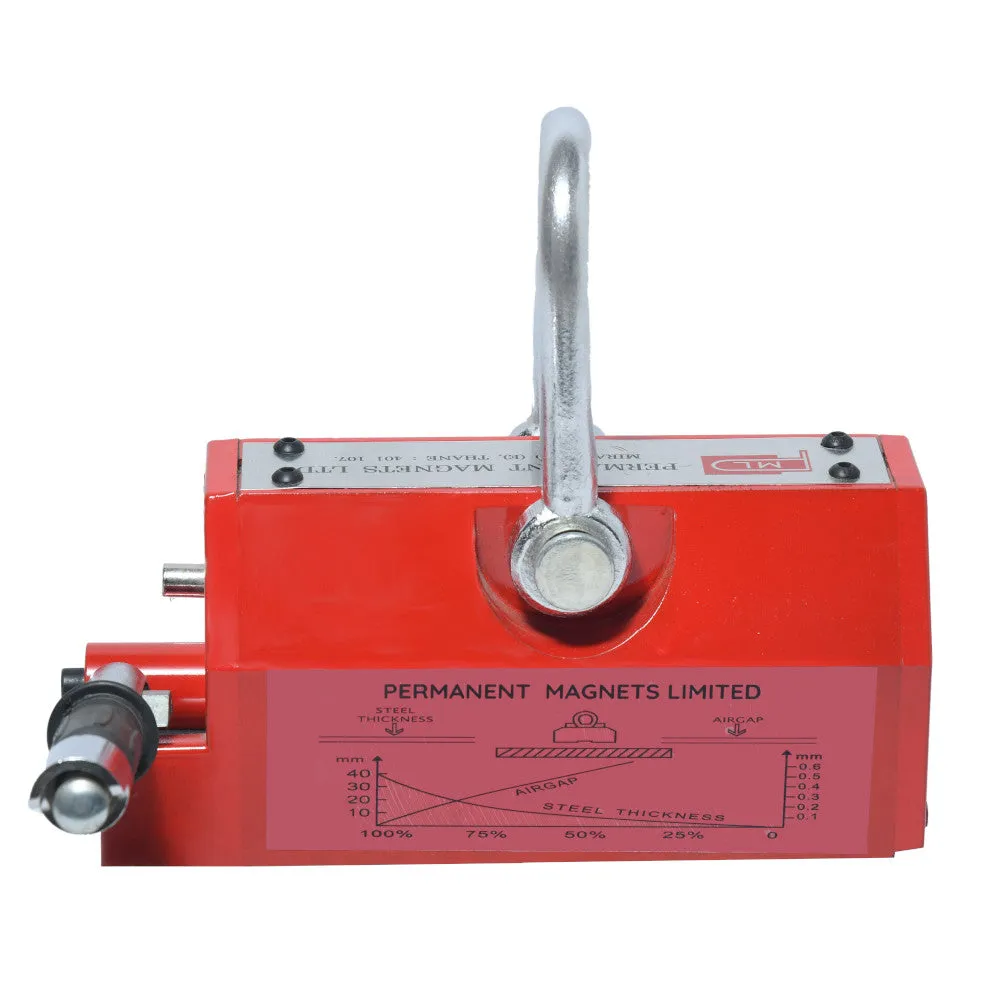
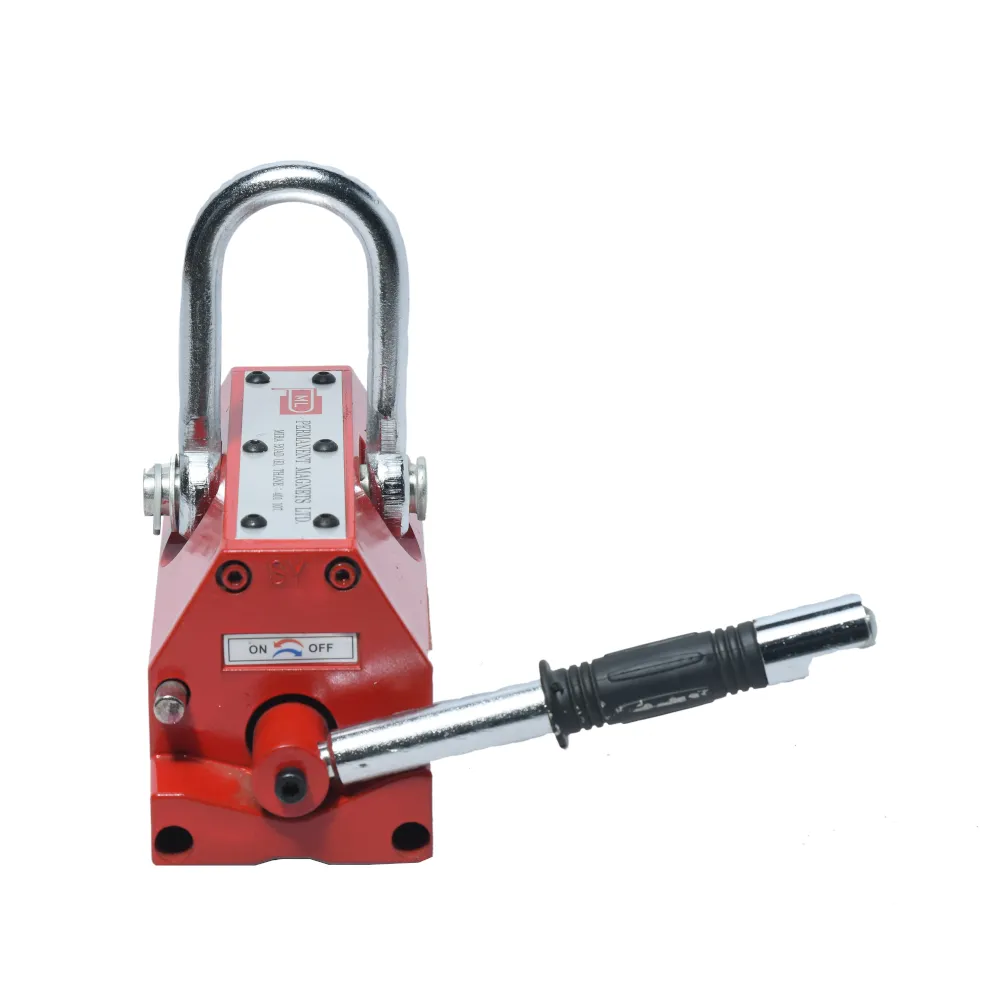
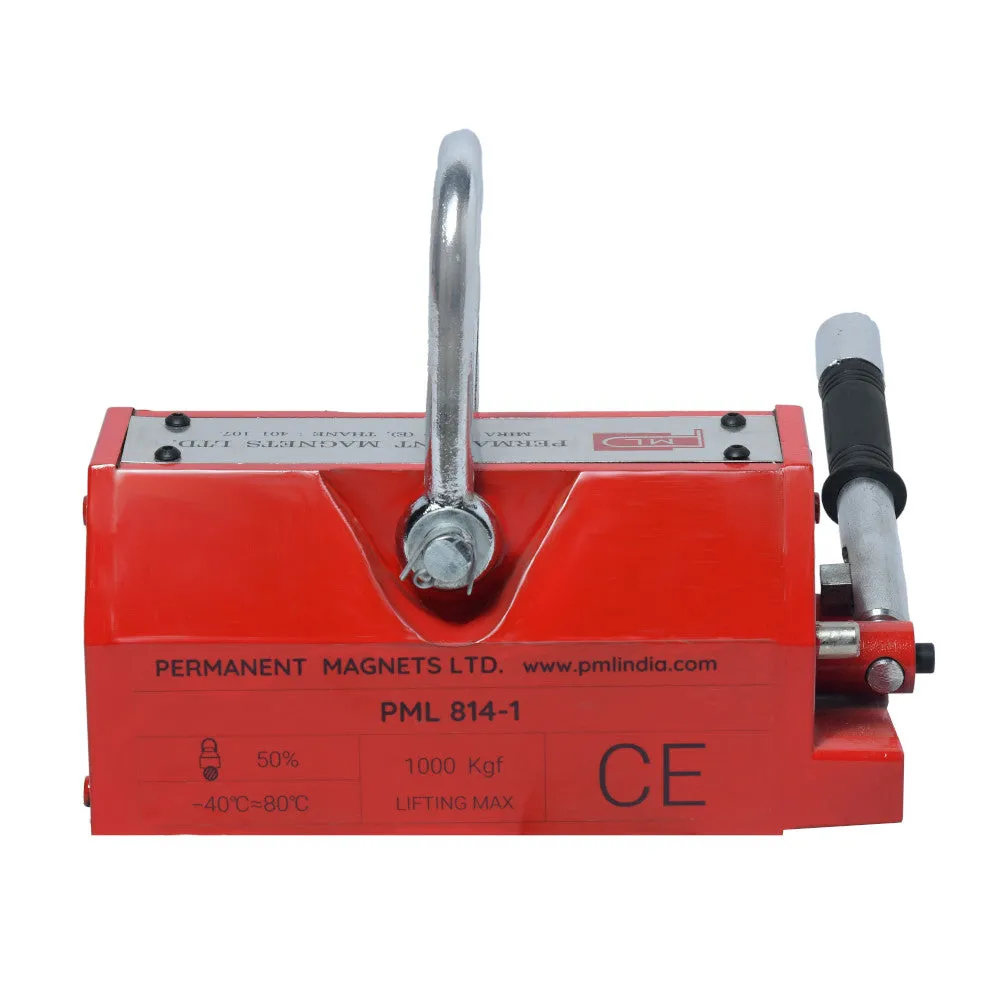
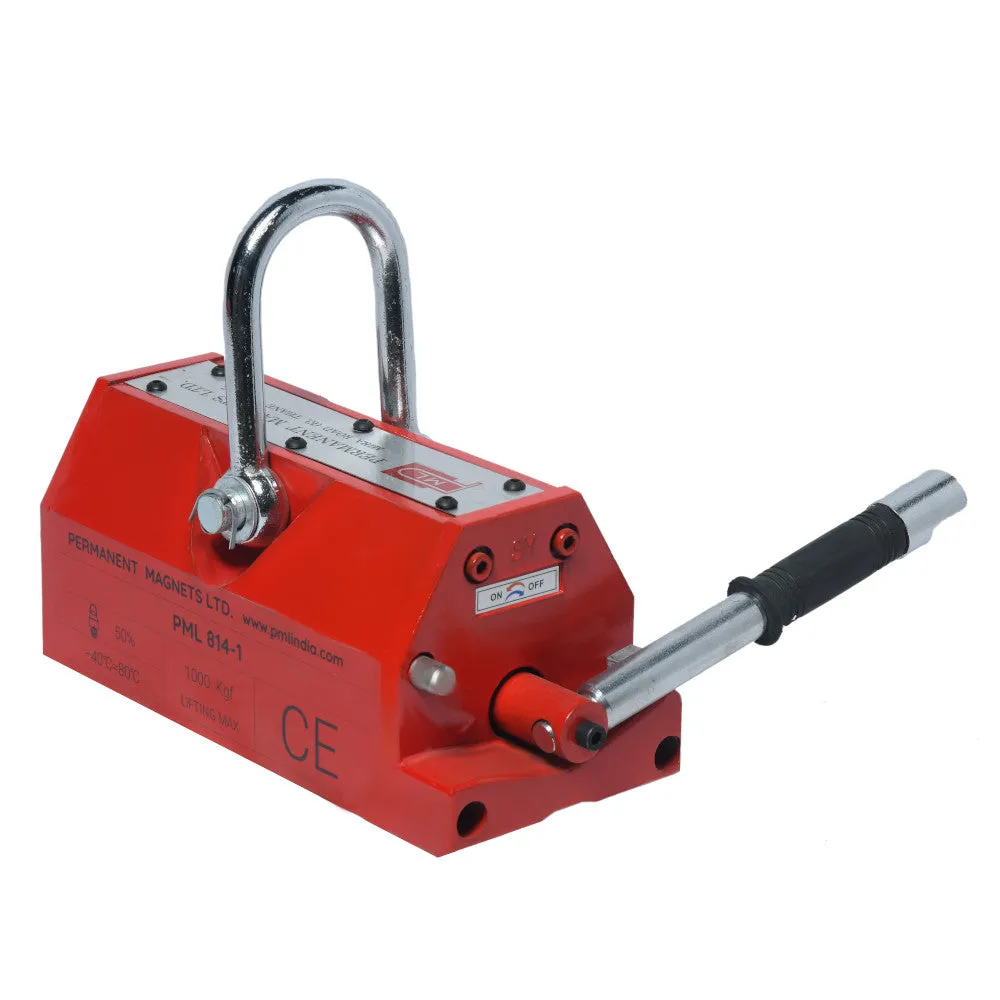
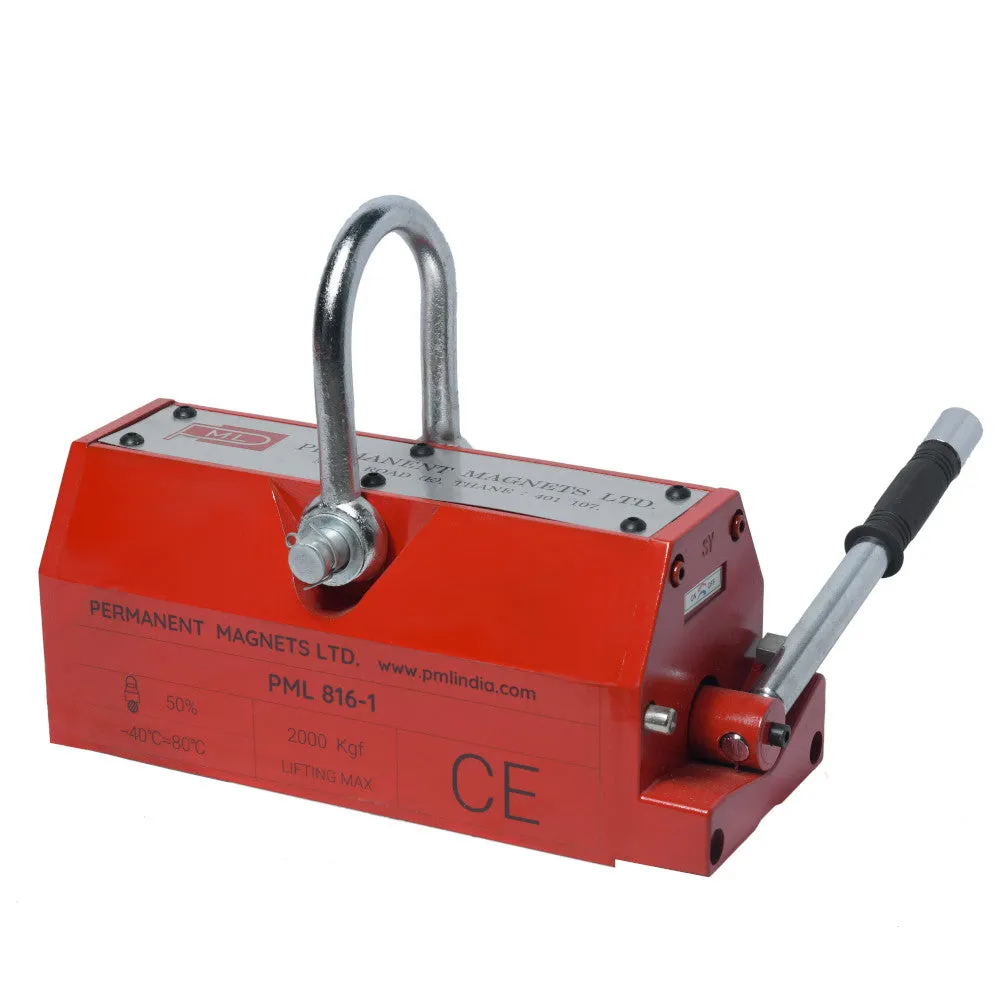
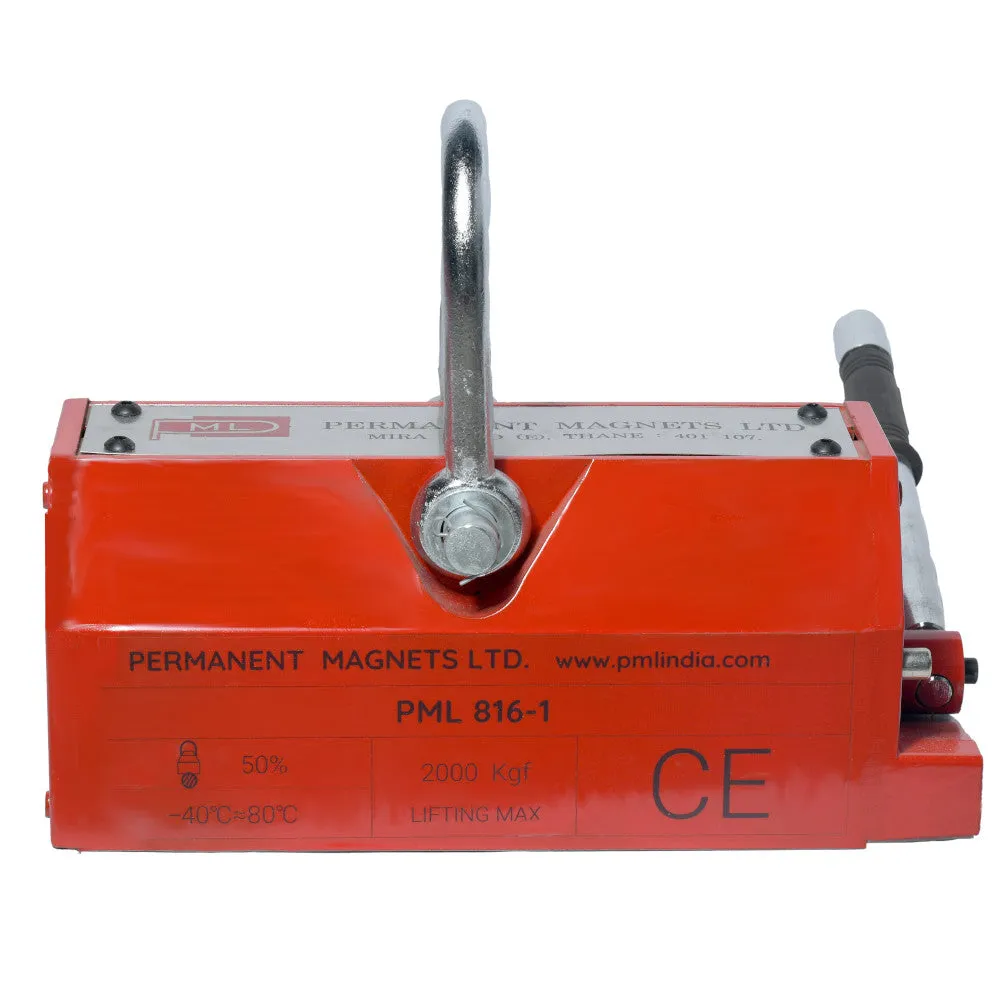
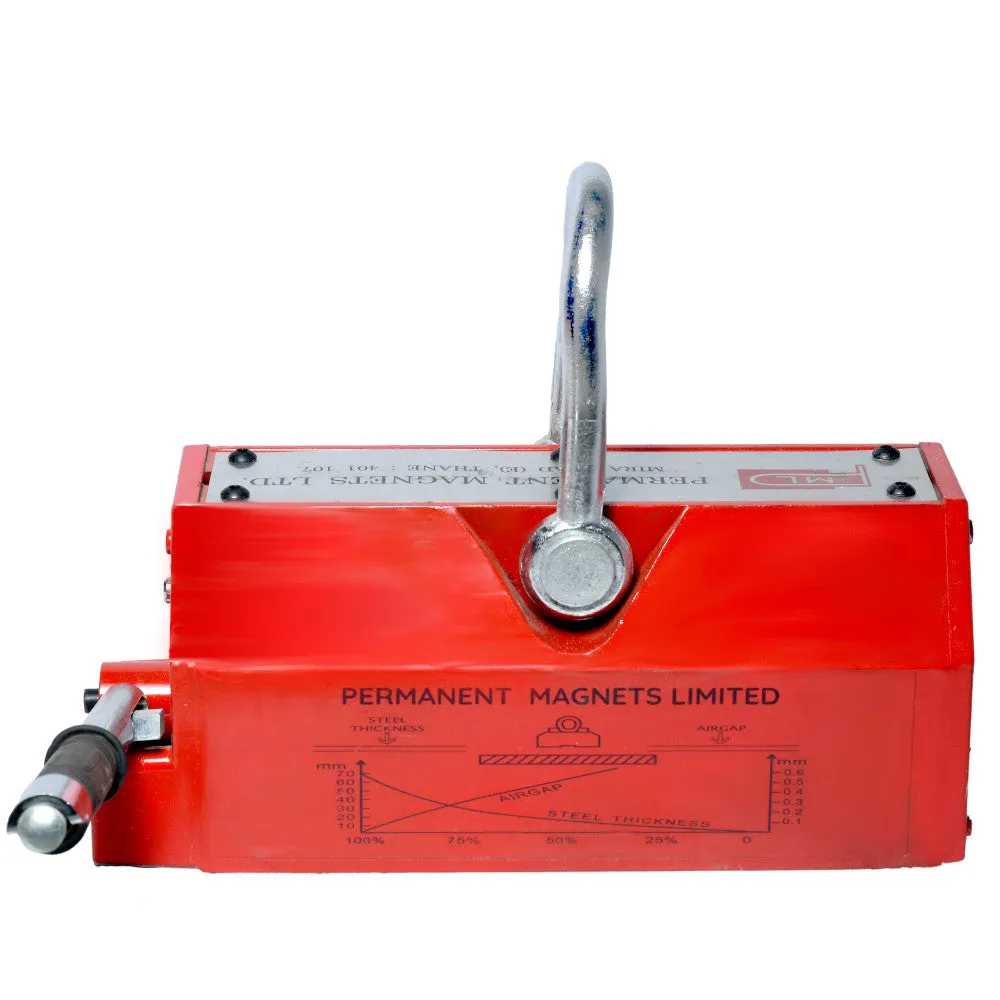
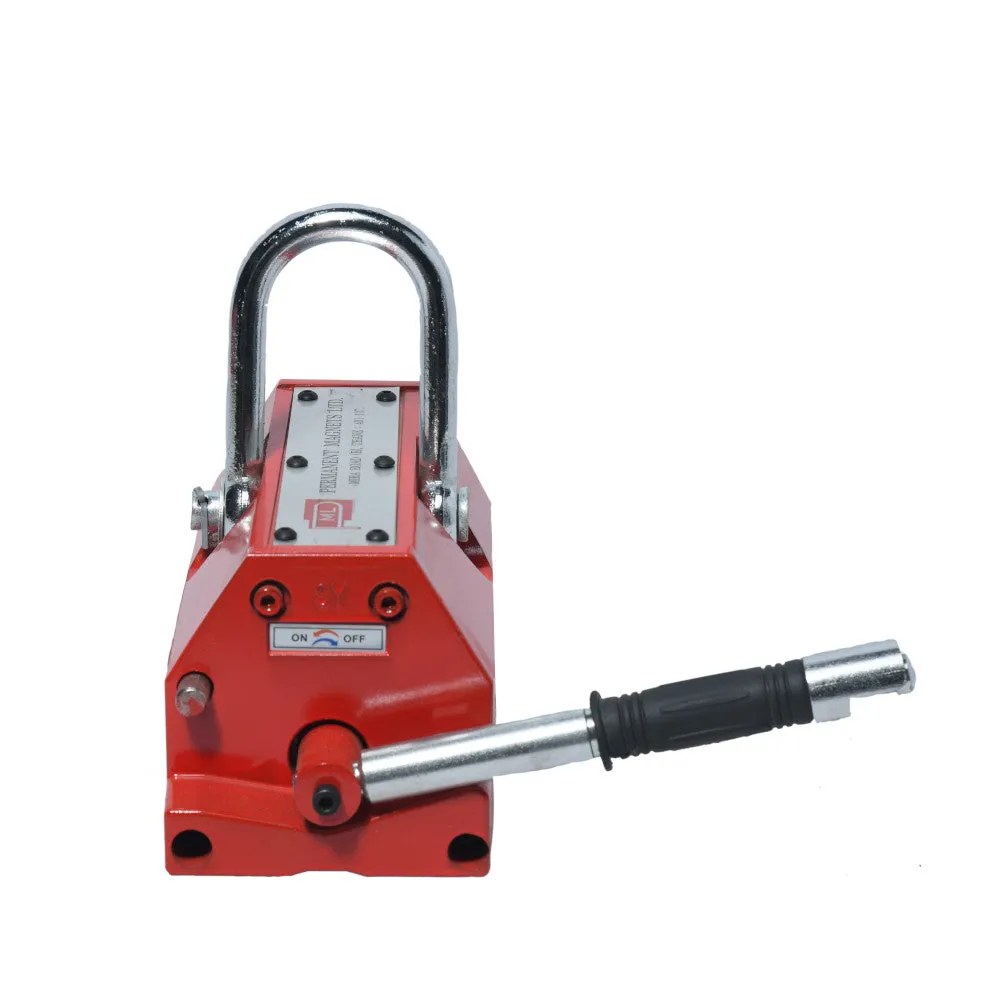
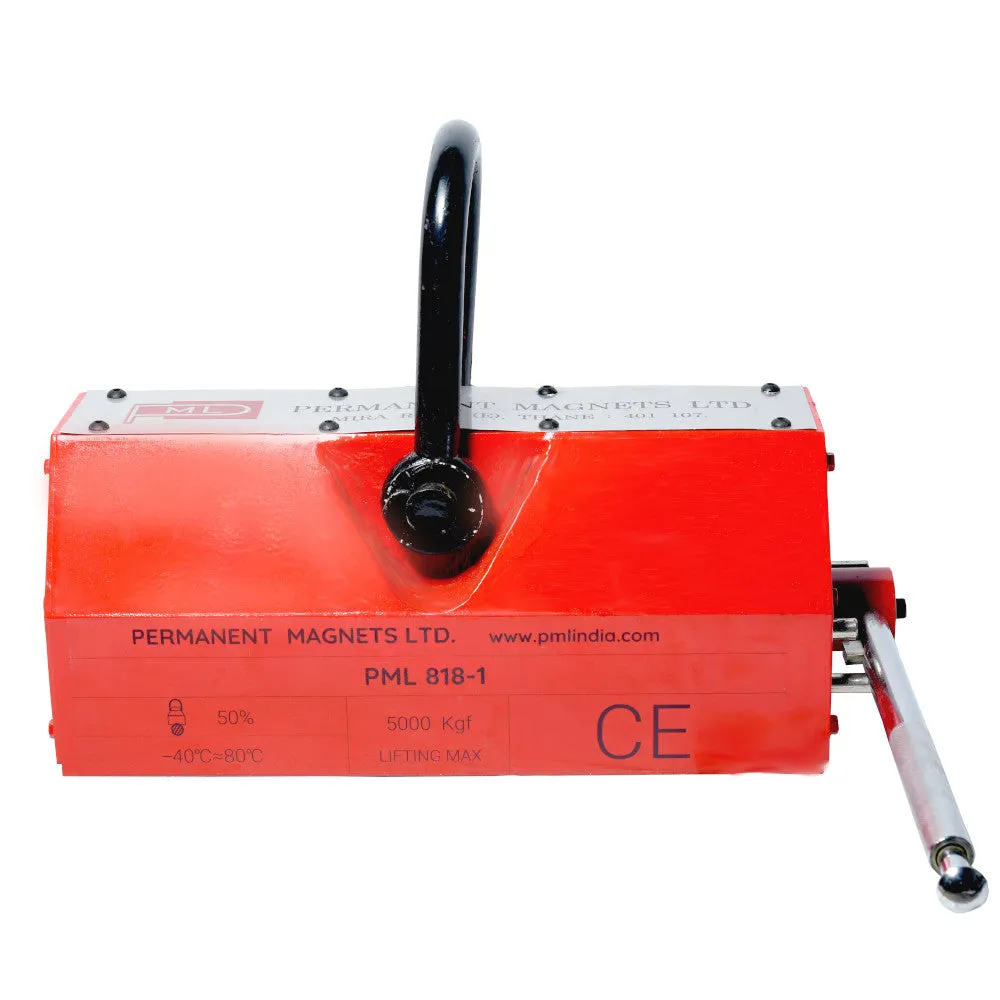
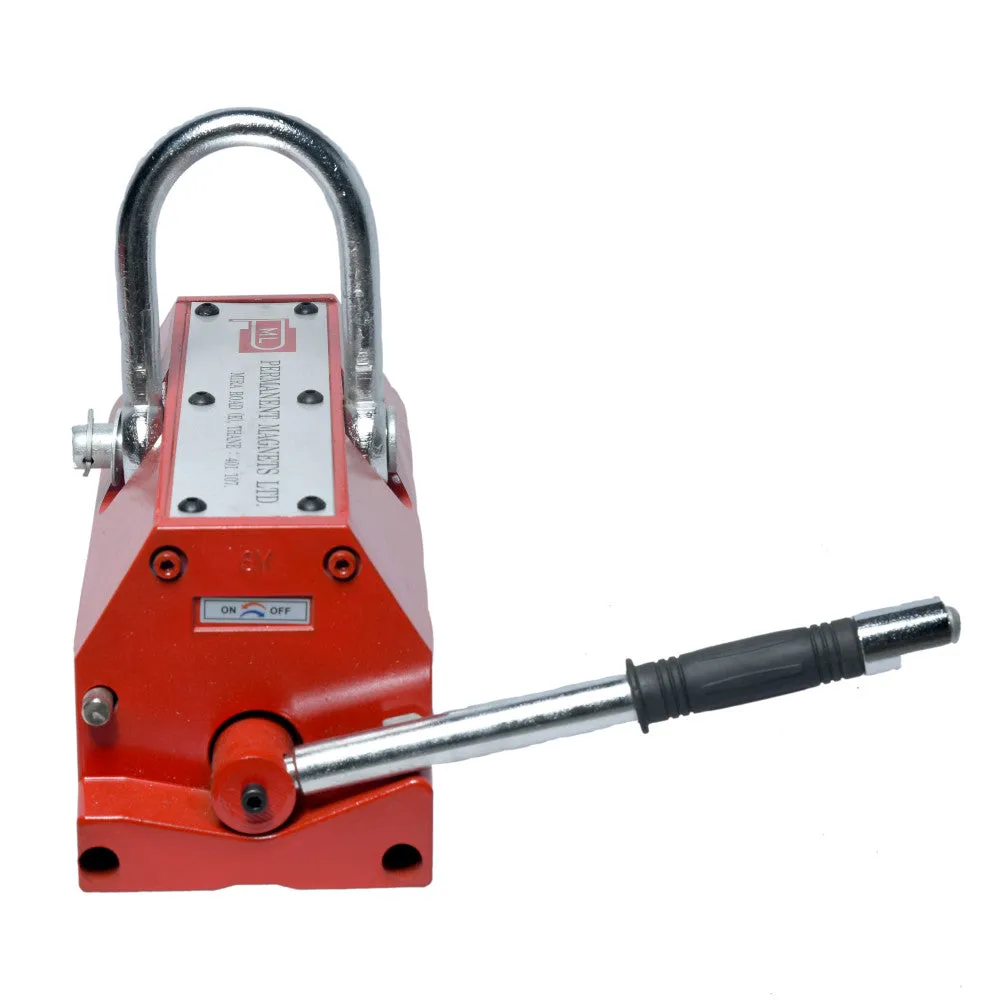
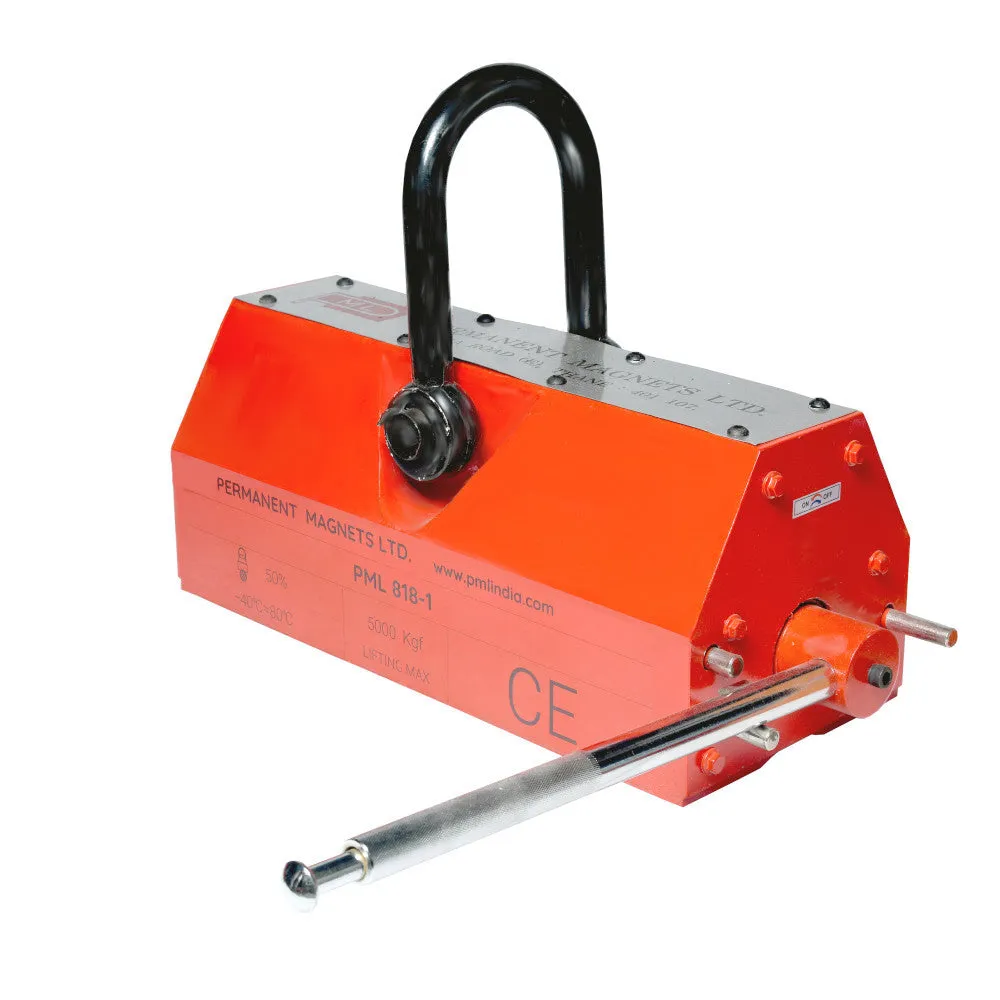
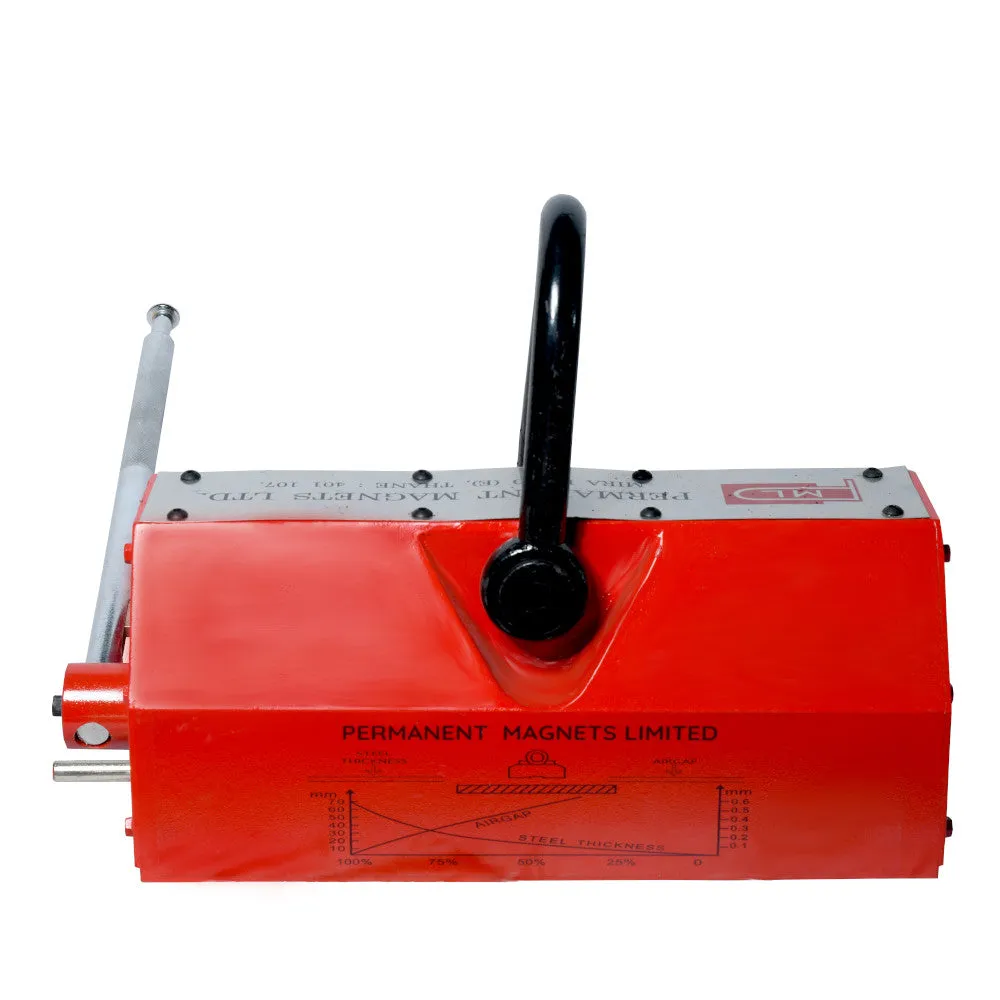
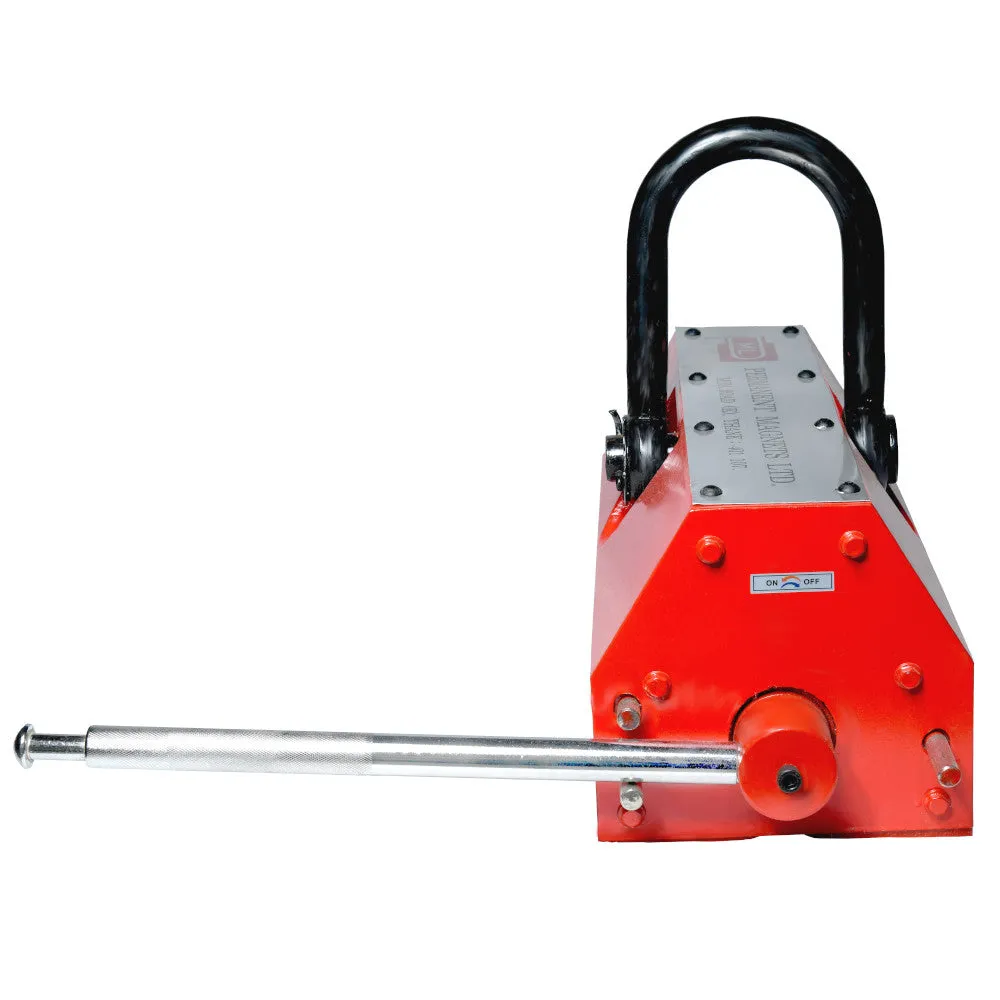
About Magnetic Lifters:
Magnetic lifters, also known as magnetic lifting devices or magnetic lift systems, are specialized lifting tools used to handle and transport ferromagnetic materials. Permanent magnetic lifters have a fixed magnetic field and do not require an external power source, making them simpler in design.
Magnetic lifters offered by Permanent Magnets Limited (Brand “PML”) have a lifting capacity ranging from 400kg to 5tons. Here's a breakdown of the lifting capacity options you mentioned:
- Minimum Capacity: 400kg
- Maximum Capacity: 5 tons (or 5000kg)
It's important to note that these lifting capacities refer to the maximum weight the magnetic lifters can handle safely. When considering a magnetic lifter for a specific application, it's crucial to ensure that the lifter's lifting capacity matches or exceeds the weight of the intended load.
Multiple magnetic lifters can also be used for lifting / holding of big size ( L x W ) steel plates
| PERMANENT MAGNETIC LIFTER MODELS WITH 2 TIMES FACTOR OF SAFETY | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model No. | Lifting Capacity | Dimension (In mm) | MS Sheet Thickness Recommendation | Self Weight | |||
| Flat Surface | L | B | H | R | (In Kgs) | ||
| 812-1 | 400 Kg. | 157 | 90 | 93 | 210 | ≥ 10 | 10 |
| 813-1 | 600 Kg. | 210 | 120 | 115 | 230 | ≥ 20 | 20 |
| 814-1 | 1000 Kg. | 256 | 142 | 135 | 280 | ≥ 25 | 36 |
| 816-1 | 2000 Kg. | 347 | 166 | 165 | 360 | ≥ 35 | 68 |
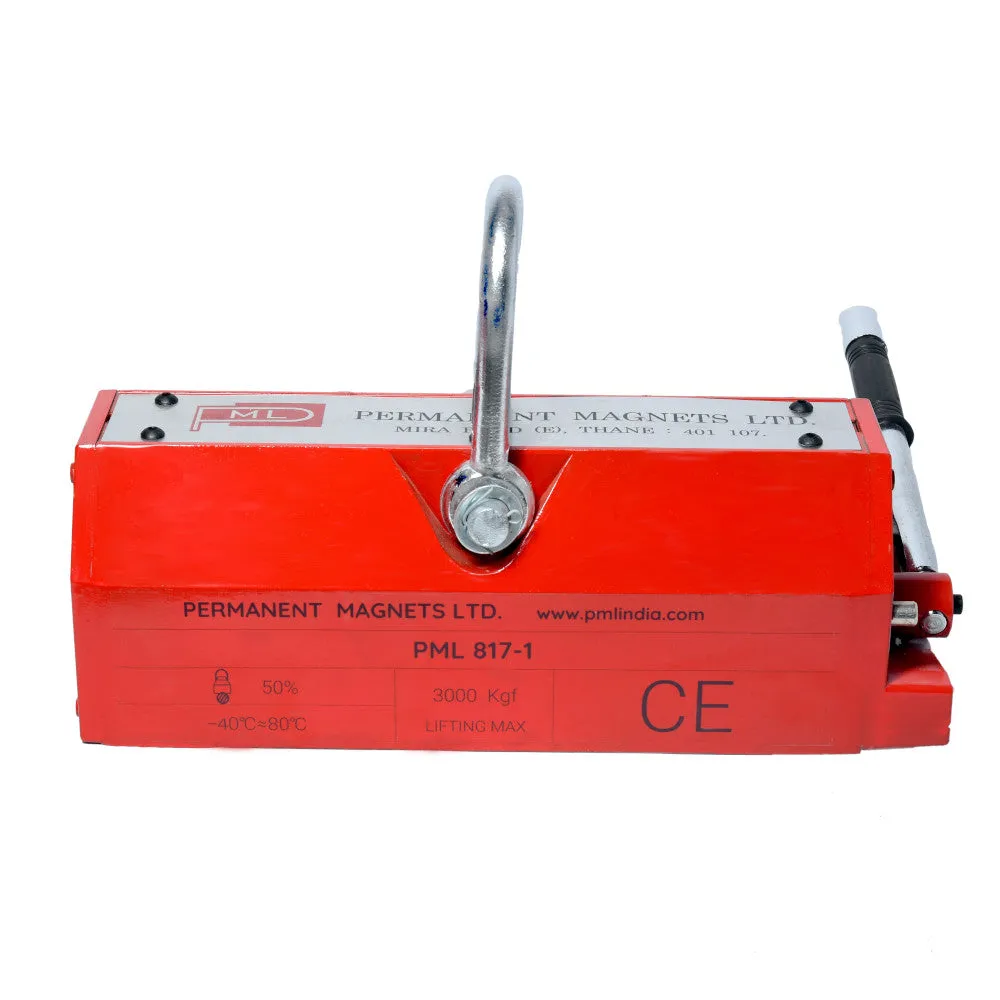
| 817-1 | 3000 Kg. | 432 | 166 | 165 | 360 | ≥ 35 | 92 |
| 818-1 | 5000 Kg. | 530 | 225 | 220 | 590 | ≥ 55 | 198 |
Main usage and characteristics:
Magnetic lifters can be used in various industries and applications where lifting and handling of ferromagnetic materials are required. Here are some common areas where magnetic lifters are utilized:
- Manufacturing and Fabrication:
Magnetic lifters are commonly used in manufacturing and fabrication industries to handle metal sheets, plates, beams, pipes, and other ferromagnetic components. They help streamline material handling processes and improve efficiency.
- Construction:
Magnetic lifters find applications in construction sites for lifting and positioning steel structures, beams, columns, and other metal elements. They facilitate the safe and efficient installation of metal components during construction projects.
- Warehousing and Logistics:
Magnetic lifters are employed in warehouses and logistics operations for handling and transporting metal products and materials. They aid in loading and unloading operations, as well as organizing and stacking metal items.
- Scrap Metal Industry:
Magnetic lifters play a crucial role in the scrap metal industry. They are used to efficiently separate and handle ferromagnetic materials from non-magnetic waste, simplifying the sorting and recycling processes.
- Metal Recycling:
Magnetic lifters are employed in metal recycling facilities to lift, transport, and process ferrous metals. They assist in material separation and preparation for further recycling processes.
- Shipbuilding and Offshore Industries:
Magnetic lifters are utilized in shipyards and offshore industries for handling heavy metal plates, sections, and equipment during shipbuilding, maintenance, and repair operations.
- Automotive and Machinery Manufacturing:
Magnetic lifters are used in the automotive and machinery manufacturing sectors for lifting and positioning metal components, such as engine blocks, chassis, and large machinery parts.
- Mining and Extractive Industries:
Magnetic lifters can be employed in mining and extractive industries for handling and transporting iron ore, minerals, and other ferromagnetic materials.
- Foundries and Metal Casting:
Magnetic lifters are utilized in foundries and metal casting processes to handle and position metal molds, cores, and castings.
It's important to consider the specific lifting capacity, dimensions, and operating conditions when selecting a magnetic lifter for a particular application. Additionally, it's advisable to follow safety guidelines and training protocols to ensure safe and effective use of magnetic lifters in any given industry or application.
Main structure and parameters:
The main structure and parameters of a Magnetic Lifters using Nd-Fe-B high-performance permanent magnetic material can be described as follows:
- Permanent Magnetic Material:
The magnetic lifter utilizes Nd-Fe-B high-performance permanent magnetic material. Nd-Fe-B magnets are known for their exceptional magnetic properties, providing a very strong magnetic field within the magnetic circuit.
- Core Shaft:
The crane has a core shaft that can be switched on or off using a handle. This feature allows the operator to control the magnetism of the lifter without the need for a continuous power supply.
- Magnetic Circuit:
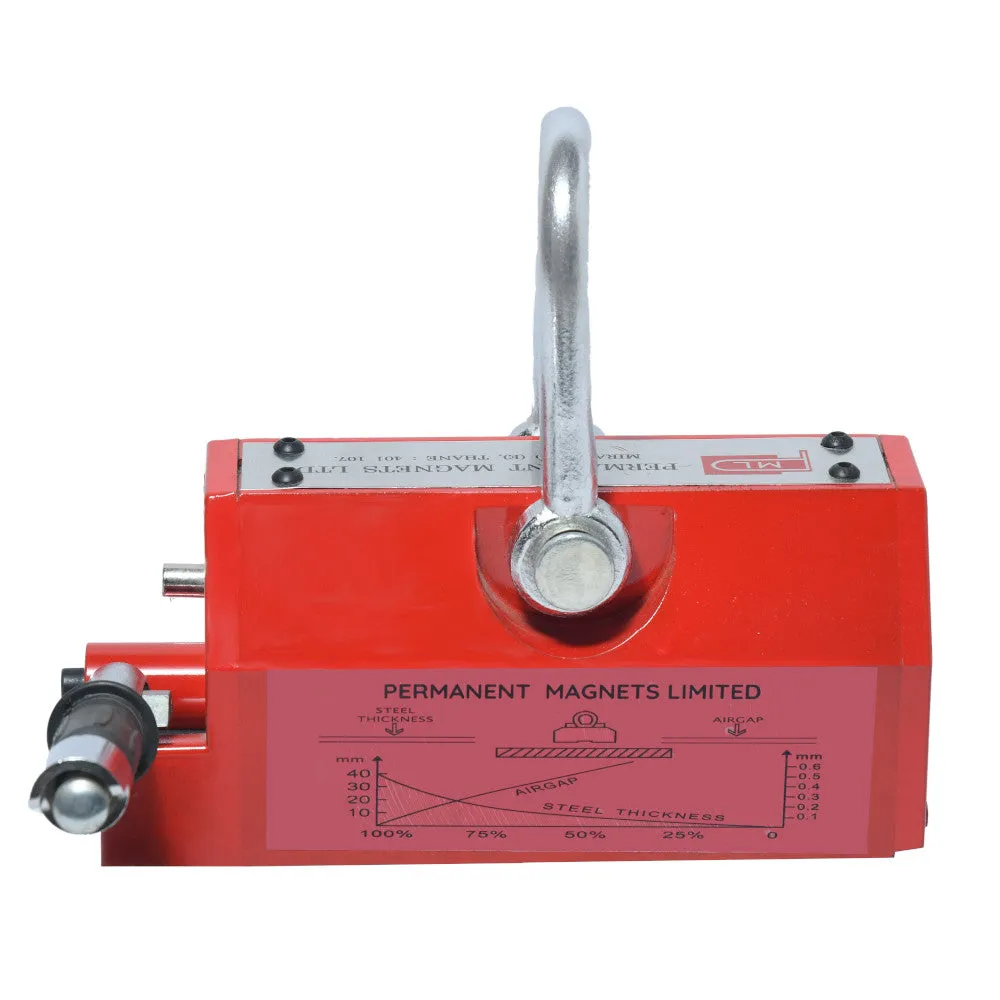
The magnetic lifter's bottom portion generates a strong magnetic field when activated. This magnetic field forms a pair of longitudinal magnetic poles that firmly attract and hold iron workpieces.
- Attraction Surface:
The attraction surface of the crane is equipped with a V-shaped groove. This design feature allows the lifter to accommodate both plank-shaped and column-shaped workpieces, enhancing its versatility.
The choice of the type:
When selecting a magnetic lifter, several factors should be considered to ensure the appropriate type is chosen. Here are some key factors to take into account:
- Workpiece Thickness and Weight:
The thickness and weight of the workpiece play a crucial role in selecting the right magnetic lifter. Different lifters have varying lifting capacities and are designed to handle specific weight ranges. It's important to choose a lifter that can safely support the weight of the workpiece.
The conversion reference of the thickness and lifting power:
Material Thickness Load capacity ratio mm inch 818-1
(5000kgs)817-1
(3000kgs)816-1
(2000kgs)814-1
(1000kgs)813-1
(600kgs)812-1
(400kgs)T1 UP90 UP3.54 100% 100% 100% 100% 100% 100% T2 80 3.15 95% T3 75 2.95 90% T4 70 2.76 85% T5 65 2.56 80% T6 60 2.36 75% T7 55 2.16 70% 95% T8 50 1.97 65% 90% 95% T9 45 1.77 60% 85% 90% T10 40 1.57 55% 80% 85% T11 35 1.38 50% 70% 75% 90% T12 30 1.18 40% 60% 65% 80% T13 25 0.98 30% 50% 55% 70% 90% T14 20 0.79 20% 40% 45% 60% 75% 90% T15 15 0.59 16% 30% 35% 50% 60% 70% T16 10 0.39 10% 20% 25% 35% 45% 50% T17 5 0.2 6% 10% 15% 20% 25% 30% - Gap between Workpiece and Magnetic Lifter:
The gap between the workpiece and the magnetic lifter is also a critical consideration. Some magnetic lifters require direct contact with the workpiece, while others can handle a certain gap distance. It's essential to choose a lifter that can effectively generate the required magnetic force within the specified gap distance.
- Material of the Workpiece:
The material composition of the workpiece is significant as certain magnetic lifters are specifically designed to handle ferromagnetic materials like iron or steel. For non-ferromagnetic materials such as aluminum or copper, alternative lifting methods may be more suitable.
- Area of Attraction:
The size and shape of the workpiece's attraction surface and the area covered by the magnetic lifter should be taken into account. The lifter's magnetism should adequately cover the attraction area to ensure a secure grip on the workpiece.
- Weight Balance:
The weight distribution and balance of the workpiece are important for safe lifting. It's necessary to choose a magnetic lifter that can maintain stability and prevent any tilting or uncontrolled movements during lifting.
- Surface Roughness:
The roughness degree of the workpiece's surface may affect the gripping ability of the magnetic lifter. Smoother surfaces generally provide better contact and stronger magnetic attraction. For rough or uneven surfaces, special considerations may be needed, such as using lifters with specific surface features or using additional clamping mechanisms.
The surface roughness of the material (Fx), the material (Mx) and the lifting power conversion,the load capacity and the roughness of the surface.
The conversion formula of the lifting range - (Tx*Fx*Mx rated lifting weight Kg).
By carefully considering these factors, you can select the relevant type of magnetic lifter that matches the requirements of your specific application. It's recommended to consult the manufacturer's guidelines, specifications, and technical data to ensure the chosen lifter is suitable for the intended workpiece and operating conditions.
The operation and use:
- A general outline of the installation process:
- Identify the Suitable Mounting Surface:
Choose a mounting surface that is strong, flat, and capable of securely supporting the weight of the magnetic lifter and the load it will be handling. Ensure that the surface is clean and free from any debris or contaminants.
- Position the Magnetic Lifter:
Place the magnetic lifter on the mounting surface, aligning it according to the desired lifting direction and the location of the load to be lifted.
- Secure the Lifter in Place:
Depending on the design of the magnetic lifter, it may have mounting holes or other attachment mechanisms. Use appropriate bolts, screws, or other fasteners provided by the manufacturer to securely attach the lifter to the mounting surface. Follow the manufacturer's guidelines and torque specifications for proper installation.
- Test and Verify Stability:
Once the lifter is installed, perform a stability check to ensure it is securely fastened and stable. Gently apply pressure or attempt to move the lifter to verify its stability and the effectiveness of the mounting.
- Test Lifting Functionality:
Before using the magnetic lifter to lift any load, test its lifting functionality in a controlled manner. Ensure that the lifter can generate the required magnetic force and effectively hold and release the load as intended.
- Identify the Suitable Mounting Surface:
- Lifting Power Estimation:
Consider the practical situation, including the workpiece's material, thickness, and surface quality, and use conversion factors (such as Tx, Fx, and Mx) provided by the manufacturer to estimate the lifting power of the crane. This estimation helps determine the crane's actual hoisting capacity.
- Attracting Area:
To maximize the lifting power, try to increase the attracting area between the crane and the workpiece. A larger attracting area can enhance the magnetic grip and lifting capacity.
- Handle Operating Power:
The handle operating power may vary depending on the degree of the crane's lifting capacity being utilized. Lifts involving column-shaped or thin workpieces with rough surfaces (roughness above 6.3um) and smaller attracting areas may require increased handle operating power.
- Working Environment Conditions:
Ensure that the working environment of the permanent magnetic crane meets certain conditions, including a temperature not exceeding 80°C, no violent shaking or impact, and the absence of metal-eroding agents in the vicinity.
- Gravity Center and Balance:
When hoisting a workpiece, make sure to lift it from its gravity center to maintain balance. Switch the handle from OFF to ON after confirming that the slide key is locked. Ensure smooth and steady movement of the lifter to avoid any shaking that could lead to the workpiece dropping or accidents.
- Hoisting Column-Shaped Workpieces:
When hoisting column-shaped workpieces, ensure that the V-shape on the crane bottom contacts the workpiece. However, note that the hoisting capacity for column-shaped workpieces is typically reduced to 30%-50% of the rated hoisting capacity, with the specific reduction related to the diameter of the column workpiece.
- Post-Hoisting Operation:
After completing the hoisting operation, detach the slide key of the handle from the positioning lock and return the handle to the free position. Shut off and remove the lifter.
In principle, for efficient and safe lifting, the length of the workpiece should not exceed 3000mm (3 meters) when using a single lifter. This guideline is likely specified by the manufacturer based on the lifter's design and engineering considerations.
Alternatively, if the workpiece exceeds the recommended length limit, the use of multiple lifters can be a viable solution. The picture you mentioned might illustrate the use of multiple lifters in tandem to handle longer workpieces. This approach helps distribute the load and ensures stability during the lifting operation.
The maintenance and safety:
Maintenance and safety are crucial aspects of operating a permanent magnetic lifter. Here are the guidelines you provided:
- Idle Load:
It is prohibited to have an idle load on the permanent magnetic lifters. This means the lifter should not be operated without a load attached. Operating the lifter without a load can affect its performance and may lead to accidents.
- Rated Weight and Overloading:
The permanent magnetic lifter should only be used within its rated weight capacity. Overloading the lifter is strictly forbidden to prevent accidents. It is important to ensure that the weight of the load being lifted does not exceed the lifter's specified capacity.
- Safety during Operation:
It is strictly forbidden to stand under or pass through the hoisted workpiece during lifter operation. This safety measure is in place to prevent injuries or accidents caused by falling objects.
- Moving Work:
Only start the moving work of the lifter after the workpiece is safely lifted and secured in the air. This ensures stability and minimizes the risk of unintended movement or accidents during the lifting process.
- Handle Operation:
Do not turn the handle of the lifter when the lifter's bottom does not have a magnetized workpiece. The handle should be operated only when the lifter is in contact with a magnetizable load to ensure proper functioning.
- Regular Inspection:
Regularly check the slide-key and positioning bolt to ensure they are reliable, locked, and secure. These components play a critical role in the safe operation of the lifter and should be inspected periodically.
- Clean and Flat Absorbing Surface:
Keep the absorbing surface of the permanent magnetic lifter clean and flat. Regularly remove any impurities or debris that may affect the performance or gripping ability of the magnetic surface.
- Avoid Striking or Impact:
It is important to avoid striking or impacting the permanent magnetic lifter during operation. Such actions can negatively impact the lifter's performance, stability, and safety.
- Demarcation and Testing:
After putting the lifter into use, it is recommended to perform demarcation and testing every two years. This ensures the ongoing safety and reliability of the lifter. Consult the manufacturer's guidelines for specific testing and maintenance procedures.
- Idle Load:
By following these maintenance and safety guidelines, you can help ensure the proper functioning, longevity, and safety of the permanent magnetic lifter during its operation.